제목
Depositing Material That Saves Time and Cost
Office of Information | 2019-01-29 | 조회 10471
본문 내용
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is an excellent photocatalyst capable of oxidizing substances by absorbing light. It is widely used as a coating material for semiconductors and solar cells, as well as disinfectants, deodorizers and antibacterial agents.
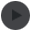
In industry, chemical vapor deposition and vacuum plasma deposition, such as the sol-gel process, have been generally applied to make TiO2 thin films, but such methods require high vacuum. Recently, low-temperature vapor deposition has been attracting interest as flexible materials are vulnerable to heat, but the techniques have shown a slow speed and low quality.
To overcome this, CBNU Professor Se Youn Moon’s team (Dept. of Applied Plasma Engineering and Dept. of Quantum System Engineering) has developed a high-speed vacuum deposition technology of high-quality titanium dioxide using low-temperature plasma at normal pressure.
They utilized low-temperature, atmospheric-pressure plasma technology to develop a technique to rapidly deposit TiO2 in an open space. The results showed a two- to three-fold improvement in chemical vapor deposition over the same process system and better performance in terms of deposition quality.
The research results were published in the November issue of Scientific Reports.
“Not only improving the deposition speed, the technology is also effective in controlling impurities such as carbon in the deposition layer through controlling atmospheric plasma properties,” said Seongchan Kang, one of the first authors, confidently. “And it can be a starting point for high purity TiO2 deposition technology.”
In addition, the technology significantly reduces the time and cost by adopting a simple low-temperature atmospheric pressure plasma process. In contrast, the existing research requires expensive equipment, such as a vacuum device and heating parts, as well as a complicated process. The new technology can be expanded to meter-level, thus applied to the industry.
Rodolphe Mauchauffé, the other first author of the research, drew attention worldwide by presenting the research results and receiving an ‘excellent presentation prize’ at the Association of Asia-Pacific Physical Societies Division of Plasma Physics (AAPPS-DPP) in November.
The research was made possible with the participation of Seongchan Kang, Rodolphe Mauchauffé, Yong Sung You and Se Youn Moon, with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea and POSCO Research Institute.